
Some racemose inflorescence examples are mustard, larkspur, snapdragon etc. The flowers stay open for a shorter time, and occurrence of this type of flowering arrangement is shorter. The growth of flowers is terminal and one-sided.įlower clusters are arranged in a centripetal way where young flowers are at the centre.įlowers are arranged in a centrifugal manner where older ones are at the centre. The growth of the main stem ends in the development of a flower at the top.Īrrangement of flowers are in acropetal order. The main stem experiences continuous growth. Difference Between Racemose Inflorescence and Cymose Inflorescence You can go through the table to quickly revise the main characteristic features. The table given below shows the differences between these two inflorescences. It is easy to confuse the characteristics of the two types and consequently, it is vital you note their differences. The two main types of inflorescence are racemose and cymose. The globose head is also known as glomerule. The flowers are either sessile or sub-sessile which are arranged in a centrifugal order like a globose head. The formation is similar to a raceme head. Examples are calotropis, hamelia patens etc.Ĭymose Capitulum or Head – In this type, the peduncle or the main stem is in the shape of a circular disk.

It looks similar to umbel type inflorescence, but the difference between the two is that terminal flower matures or opens first. Then from the base of this terminal flower, two or sometimes more than two lateral flower producing branches originate. Polychasical or Multiparous Cyme – Here the central axis or peduncle ends in a flower called the terminal bud. Examples of dichasial cyme include saponaria, jasmine, teal ixora and so on. The lateral branches may, in turn, produce two other branches. However, two lateral branches originate from the main stem at the same time, and they too stop growing after producing a flower.
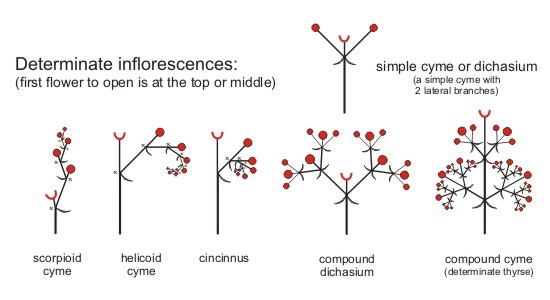
Sympodial – It is a type of monochasial cyme where stems which are curved or zig-zag in the beginning but later on become straight and multiply to form the central axis.īiparous or Dichasial Cyme – In this type of inflorescence, the main stem stops growing after the development of a terminal flower. Two types of scorpioid include cincinnus and rhipidium. Scorpioid – when branches grow alternatively on both sides, it is known as monochasial scorpioid cyme. Notably, there are two types of helicoid – drepanium and bostryx. Helicoid – In this type of uniparous cyme, the branches keep growing on the same side only and ultimately form a helix. Monochasial cyme can be classified into three types. It produces one lateral branch at a time which also terminates after developing one flower and another succeeding branch at a time. Uniparous or Monochasial Cyme – In this case, the peduncle or main stem produces only one flower and stops growing. These groups have been discussed in detail below, along with their individual subgroups and divisions– Types of Cymose InflorescenceĬymose inflorescence can be further divided into four different groups which are a vital part of your curricula. It means that the flowers start opening from the centre to their periphery. Consequently, flowers in cymose inflorescence open in a centrifugal mode. The flowers are arranged in a basipetal sequence, which means that flowers start maturing from apex or the top and towards the base of its stem.

It is the type of inflorescence where growth of the main stem stops after the growth of a flower. Racemose inflorescence falls under indeterminate category while cymose inflorescence is of determinate inflorescence type. In determinate inflorescence, young budding flowers can be found at the bottom, while in indeterminate inflorescence young buds are at the top. Each of these types is further classified into two other categories - determinate and indeterminate inflorescence. This arrangement of a cluster of flowers on a stem which can be a single branch or system of branches is called an inflorescence where the main stem is called a peduncle.Īdditionally, inflorescence can be classified into different types – racemose and cymose inflorescence, compound, special, mixed or verticillaster inflorescence. Some flowers like roses grow alone, and others grow in a group or cluster. In angiosperms, flowers are arranged in a specific order in each plant.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
